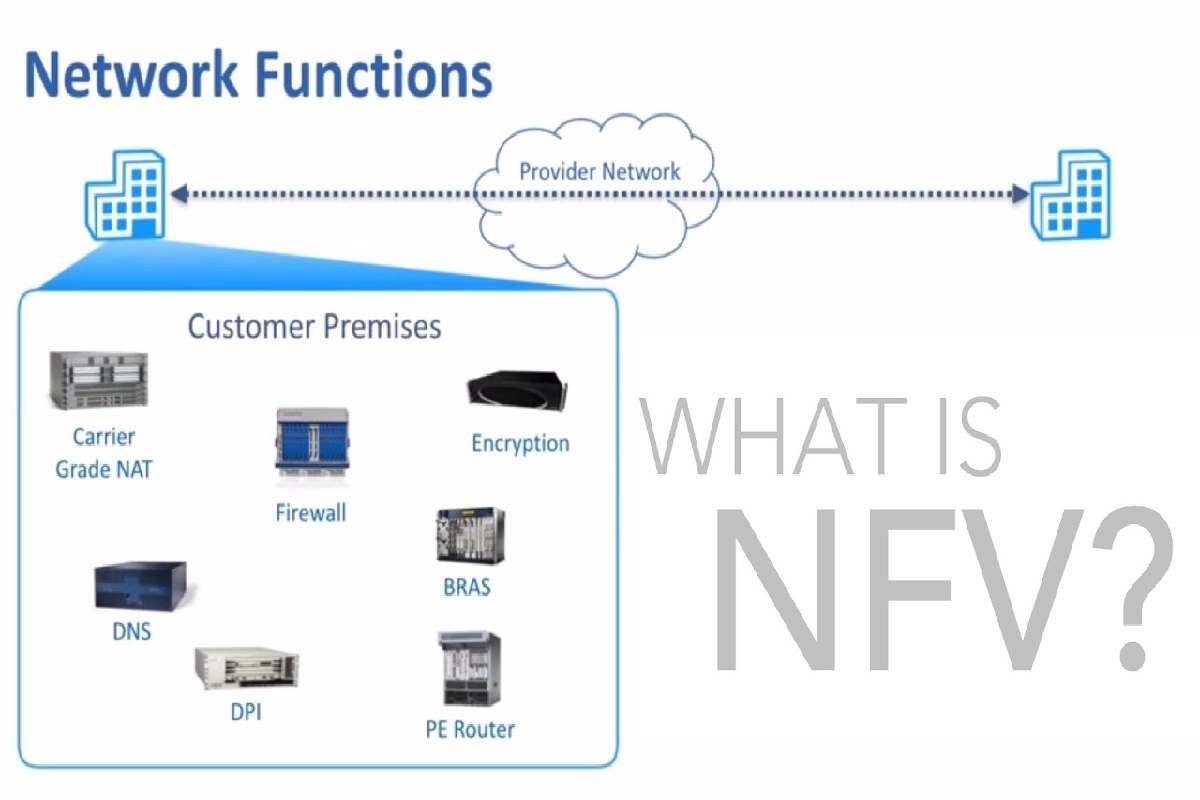
NFV networks cannot meet the consumer demand demanded by the new mobility and cloud scenarios. This article explains what NFV is, Network Function Virtualization, and how it meets today’s needs for bandwidth, flexibility, speed, and security, thereby reducing hardware costs.
In addition, the extreme competition in which companies operate today has forced them to face a digital transformation in which the network cannot remain on the sidelines.
Business users need instant and seamless access to applications from their mobile or landline devices. This is only conceivable if there is a perfect web between the entire IT architecture that makes it possible. The network confirms that the dialogue among all IT elements is optimal.
A manual and old-style network management tactic is unsustainable: purchase of dedicated hardware for each element of the network, design and configuration, IT maintenance services to ensure its operation and its adaptation to the changes that are applie in time.
If you multiply this network operation for every IT asset, it’s a time and cost investment that virtually no business can afford.
Table of Contents
How Network Virtualization Technology Works
The benefits of virtualization also apply to networks to meet new needs and implement cost-effective IT infrastructures.
Similarly, NFV (Network Function Virtualization) consists of moving the network functions of dedicated HW computers to virtual servers. This involves consolidating multiple activities on a single physical server.
When network functions endure controlled by a hypervisor (that is, virtualization software), services that require dedicated hardware can still run on standard servers. VMware vSphere ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, or Citrix XenServer are among the most widely used hypervisors.
Adding a new network role is as easy as starting a new virtual machine and shutting it down when necessary.
Differences between NFV and SDN
Furthermore, an NFV architecture remains composed of virtualized network functions (VNF):
Network function devices
Switches, routers, network admission points, customer site equipment (CPE). Computer devices connected to the network: firewalls, IDS systems, network device management systems, etc.
NAS storage
Databases or file servers connected to the network.
The virtualization of these devices follows the same principle applied to servers and workstations; they are beginning to share generic material resources. They are no longer isolate resources with dedicated hardware.
Additionally, many NFV implementations use software-defined network (SDN) drivers as part of their architecture to manage them and the end-to-end network. SDN mentions programs that control network equipment for automation follow established rules, provide services in an agile and optimal way, and balance usage and traffic as needed.
Implementation of virtualized networks: advantages
NFV implementation is complex without the cooperation of a company specializing in IT support services as a service. Network virtualization capabilities replace open-source standards for accessible performance, but the integration of existing infrastructure needs a dedicated application.
The benefits providing by NFV are more than adequate to apply it directly to updating and integrating new network needs:
- Reduction of equipment purchase costs.
- Save space, cooling, and electricity
- Quick deployments of new devices
- Maximum flexibility and scalability to meet specific network needs.
- Management automation and centralization
- Orbit Consulting Group specializes in designing and implementing IT architecture solutions for SMEs and companies in Madrid and Spain.
Also Read : 3 Reasons Why SEO Services are Still in Demand